
Have you ever stepped outside and felt that the atmosphere seemed much hotter than what your thermometer was reading? This discrepancy can be explained by the heat index. Start your exploration by using this heat index calculator to understand today’s “feels-like” temperature in your locality.
Commonly dubbed as the “feels-like” or “apparent temperature,” the heat index is a measure that explains our perception of warmth, considering both temperature and humidity levels.
Temperature alone isn’t a standalone factor dictating our comfort levels outdoors. Humidity, essentially the amount of moisture present in the air, can significantly magnify how hot we perceive temperatures to be. For instance, a temperature of 88°F on a dry day can feel tolerable, but with elevated humidity levels, it can feel like a sweltering 100°F or more.
Our body’s primary defense against overheating is sweat, which cools us down when it evaporates. However, in humid conditions, the rate of evaporation slows down, causing us to feel warmer than the actual temperature. The National Weather Service has comprehensive charts showing just how drastically humidity can skew temperature perceptions.
While the term ‘heat index’ might roll off the tongue easily during weather reports, the science behind its calculation is intricate. It’s a fusion of temperature and humidity:
Heat Index Calculation:
Heat Index = c1 + c2 * T + c3 * H + c4 * T * H + …
Variables Explained:
If the mathematics behind this seems daunting, don’t fret. You can quickly determine the heat index for your location with this heat index calculator.
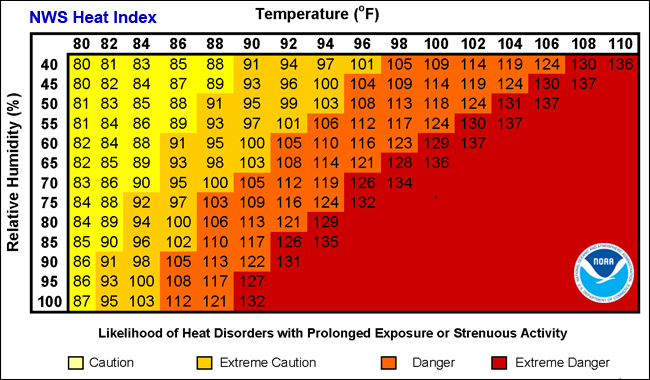
The discussion around the heat index becomes even more pertinent in the backdrop of global climate change. Rising temperatures combined with erratic humidity patterns mean that days with an unbearable heat index might be more frequent in our future. An alarming study from “Environmental Research Letters” posits that, if we continue on our current path, up to three-quarters of the world’s population could face deadly heatwaves by 2050. Discover more about this research here.
A heightened heat index isn’t just an uncomfortable experience—it poses genuine health dangers:
The CDC has reported increased hospitalizations and fatalities linked to heatwaves, especially among vulnerable populations.

As the mercury continues to rise, adapting and taking precautions become indispensable. Here’s a more in-depth look at the strategies:
Drinking water might seem like a no-brainer, but many overlook its importance. The body loses fluids more rapidly during hot conditions. Ensuring a steady intake is vital, not just during physical exertion but throughout the day. The CDC underscores the importance of fluid intake even if one doesn’t feel thirsty.
Clothing plays a pivotal role in heat management. Light-colored, breathable fabrics can significantly aid in maintaining body temperatures. Incorporate wide-brimmed hats, UV-protective sunglasses, and even UV-protective clothing to bolster defense against the sun.
Restrict heavy activities to the cooler parts of the day, either early morning or late evening. Midday sun is especially harsh, and even short exposures can lead to heat-related illnesses. If you’re looking for more in-depth guidelines on managing heat exposure, the EPA’s recommendations provide valuable insights.
With urbanization on the rise, cities become focal points in the battle against escalating temperatures. Due to the Urban Heat Island effect, cities often register temperatures much higher than their rural counterparts. According to a study in Nature Climate Change, cities must innovate and reimagine infrastructure to mitigate this effect.
Initiatives could include introducing more green spaces, white roofing (which reflects more sunlight), and enhanced urban planning focusing on airflow.
In conclusion, the heat index, while a fascinating blend of meteorology and human physiology, is more than just a scientific concept. It’s a tangible measure that impacts our daily lives. Equip yourself with knowledge and always be prepared. For real-time updates and to ensure you’re not caught off guard, make sure to bookmark this heat index calculator.